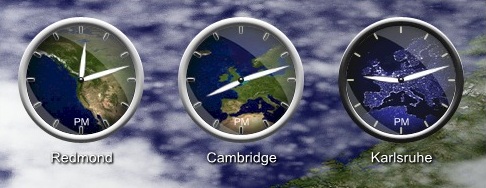
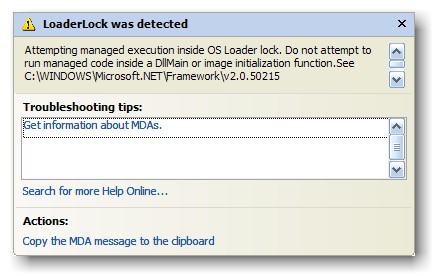
Today, I spent some minutes to enhance my desktop. I installed AveDesk 1.2 and the World Clock v0.2.0 docklet. Just rename the zipped file to .aveinst and double click it. Also ensure, that SysStats is installed before that. After spending some more time with setting up the clocks, I got only one black clock without any map in it. It took a while to find out, where the problem was. The problem is already known and depends on the regional settings of your windows. Using the German settings the system expects some floats using a format like this xxx.xxx.xxx,xx while the US layout the docklet was written for, uses xxx,xxx,xxx.xx. Unlike in the article before the World.vba there does not work, because the french settings use numbers with a format like xxx xxx xxx,xx.
This additional function and the two changes in MoveMap() should be enough for the German settings:
Function stringToFloat(strMeters)
if isNull(strMeters) then
stringToFloat = 0
exit function
end if
'US xxx,xxx.xx to DE xxx.xxx,xx
strMeters = replace(strMeters, ".", "foobar")
strMeters = replace(strMeters, ",", ".")
strMeters = replace(strMeters, "foobar", ",")
stringToFloat = strMeters
End Function
Function MoveMap()
centerX = SysStatsModel.Width/2
centerY = SysStatsModel.Height/2
latitude = stringToFloat(SysStatsModel.Meters("Latitude"))
longitude = stringToFloat(SysStatsModel.Meters("Longitude"))
' ...
End Function
You can download the modified World.vbs (as it is, without any warranty, usage on your own risk, just rename the file from World.txt to World.vbsl). Now copy the file to the folder DockletsSysStatsscriptsworld within your AveDesk directory. If you try to add more then one instances of the world clock on your desktop, copy the World.ini file from the DockletsSysStatsconfigs directory for each clock and rename it. Assign to each clock its own .ini file. Otherwise all the docklets will be the same after the next start of AveDesk.
After spending this afternoon to find out how it works, it looks pretty nice: